What Is A Scrum Burndown? This Might Surprise You!
The "Scrum Burndown Chart" (See more Burndown Chart in Scrum) is a visual
measurement tool that shows the completed
work per Sprint against the projected rate of
completion for the current project release.
Its purpose is to enable the Scrum Product
Owner, the Scrum Team, and other stakeholders
to control the progress of the project. So the
Scrum Team achieves to deliver the requested
software solution within the desired timeline.
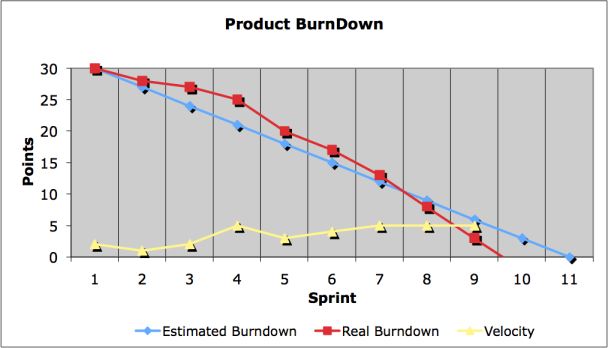
Simple Scrum Burndown Chart
The speed/rate of progress of a Scrum Team is
called "Velocity". It expresses the total number
of story points completed that the Scrum
Team delivers per Sprint (Iteration).
An essential rule to assess and calculate the
Velocity is that; Only entirely completed user
stories that precisely fulfill their Definition of
Done (DoD) are counted. The velocity calculation
shouldn't take partially completed user stories
into account. (For instance, coding of a user story
is done, but its tests are still missing)
Only a few Sprints after a new Scrum Team is
formed, the Velocity of the team can be reliably
calculated. That helps the Scrum Product Owner
to predict the throughput of the Scrum Team
better, and he or she can foresee what user
stories the Scrum Team can deliver in a given
Sprint. That would enable the Scrum Product
Owner to plan software releases more accurately,
with less surprises towards business clients and
end-users.
As a simple example: Let's assume the Velocity of
your Scrum Team is 50 story points per Sprint.
And the total amount of remaining work has
been estimated as 300 story points. Then you
can predict that you need 6 Sprints to deliver all
of the remaining user stories from the Product
Backlog.
However, in reality, the user stories in the
Scrum Product Backlog will change over the
course of the project. New stories are added,
and other stories are modified or even deleted.
In the Simple Burndown Chart, the Velocity of the
Scrum Team and the change of the scope cannot
be visualized accurately. To increase this lost
accuracy and visibility, Scrum Teams use
another type of diagram, which we call
"Extended Burndown Chart".
Extended Burndown Chart uses a bar chart
instead of a line diagram. The size of each bar
represents the total number of remaining user
stories at the beginning of each sprint. The
Velocity of the Scrum Team is subtracted from
the top bar, while changes of the Product
Backlog are presented at the bottom of the bar.
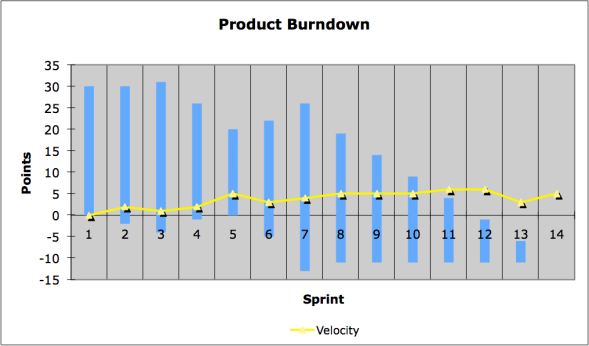
Extended Burndown Chart
Separating Velocity and Scope Changes
To get even more accurate results with the
Burndown Chart, we can also take the rate of
changes in total work into account. We call
this more precise model "Extended Burndown
Chart With Prediction”. However, we have to be
careful when using this model. The magnitude of
changes in the Product Backlog will be relatively
higher at the beginning. And yet, the rate of
changes will usually drop, and they approach
zero towards the end of the project.
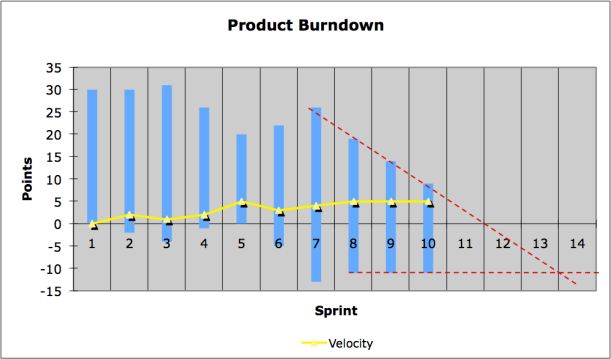
Extended Burndown Chart with Prediction
Share It With Your Colleagues and Friends to Help Them Learn:
What Is A Scrum Burndown? This Might Surprise You!
|
|

|

|

|

|
|
 SCRUM INSTITUTE™
SCRUM INSTITUTE™